2025 International Phishing Benchmarks
Australia and New Zealand
TABLE OF CONTENTS
2025 International Phishing Benchmarks
Australia and New Zealand
By Javvad Malik
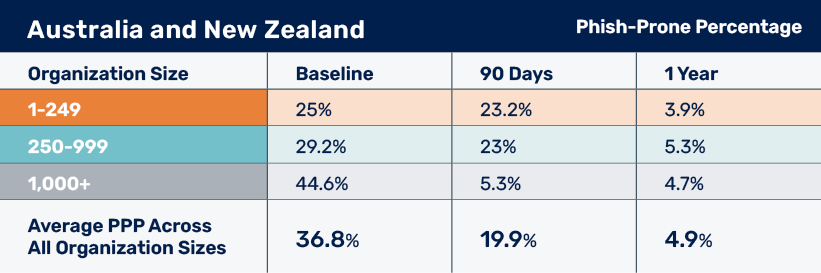
The PPP data across Australia and New Zealand presents a compelling narrative of improvement across industries and company sizes. Initially, large companies of 1,000+ exhibited the greatest vulnerability to phishing attacks globally, with the highest baseline PPP in 2024 at 44.6%. In particular, this risk was elevated in sectors such as Banking and Financial Services.
Medium and small companies, while generally less vulnerable, still demonstrated significant risk, especially in Consumer Services and Banking, with 30% or more phish-prone employees.
However, the implementation of robust SAT programs yielded significant results. After just 90 days, most sectors observed substantial reductions in their PPP, with Banking showcasing a particularly dramatic improvement of 90.4%. The most striking changes occurred after a year or more of training, where the majority of industries across all company sizes achieved single-digit PPP rates. This finding underscores the long-term effectiveness of sustained cybersecurity education.
Notably, the data highlighted interesting industry-specific trends and anomalies. The Legal sector, for instance, maintained a consistently low PPP throughout all phases, while Consumer Services persistently showed higher vulnerability. Some sectors, such as Technology and Government, exhibited slight increases in PPP for large companies in the final phase, suggesting potential areas for focused training.
”The Australian government has demonstrated a profound understanding of the critical role that cybersecurity education plays
The overall trend, however, was clear: ongoing cybersecurity awareness programs significantly enhanced an organization’s resilience against phishing attacks, regardless of its size or industry. This improvement was particularly pronounced in larger companies, which, despite starting with higher vulnerability, often demonstrated the most substantial risk reduction over time.
Evolving Threat Trends in Australia and New Zealand
Australia and New Zealand have emerged as focal points for significant trends and challenges that underscore the evolving nature of cyber threats and defense mechanisms. The Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC) and New Zealand’s National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) have been at the forefront of addressing these challenges, providing critical insights into the cybersecurity posture of the region.
The Expanding Attack Surface in Australia
One of the most pronounced trends observed in 2024 was the increasing sophistication and frequency of cyberattacks targeting critical infrastructure. These sectors, including electricity, gas, water, and waste services, alongside education and training, and transport, postal, and warehousing, were identified as particularly vulnerable.
The ACSC’s engagement, having answered over 36,700 calls through the Australian Cyber Security Hotline, underscored the heightened concern and proactive measures being adopted by organizations across the spectrum. This proactive stance was further evidenced by the response to over 1,100 cybersecurity incidents, with a notable increase in ransomware attacks, signaling a shift in tactics by cyber adversaries.
The introduction of the Cyber Security Act 2024 in Australia marked an important step forward by setting new benchmarks for smart device security and establishing mandatory reporting mechanisms for ransomware payments. This legislative action demonstrated the government’s commitment to addressing the evolving cyber-threat landscape and protecting critical infrastructure.
The Australian government’s dedication to enhancing cybersecurity awareness through the Cyber Security Awareness Support for Vulnerable Groups grants program signaled a significant milestone in the nation’s approach to digital safety. By allocating nearly $7 million AUD to over 200 recipients, the government demonstrated a profound understanding of the critical role that community-level education plays in building a resilient cyber ecosystem.
Collaboration Works to Combat Threats
Across the Tasman Sea, New Zealand’s cybersecurity challenges largely mirrored those of Australia. A report by CERT NZ (Computer Emergency Response Team) revealed that over 3,500 cyber incidents were reported in the first three-quarters of the year alone, marking a 15% increase from the previous year. These incidents encompassed a range of attacks — from phishing and ransomware to more sophisticated advanced persistent threats (APTs).
Both countries have recognized the importance of international collaboration in addressing cyber threats. The Five Eyes intelligence alliance, comprising Australia, New Zealand, the United States, the United Kingdom and Canada, has played a crucial role in sharing threat intelligence and coordinating responses to global cyber incidents. This collaborative approach has proven essential in tackling sophisticated state-sponsored attacks and transnational cybercrime networks.
Closing the Cyber Skills Gap
Australia and New Zealand have both intensified their efforts to build a skilled cybersecurity workforce to meet the growing demand for expertise in this field. Initiatives such as the 2023-2030 Australian Cyber Security Strategy and New Zealand’s Cyber Security Strategy 2019 have emphasized the need for developing talent pipelines, promoting cyber education in schools and supporting reskilling programs for professionals transitioning into cybersecurity roles.
”Despite starting with a high PPP of 85%, larger companies in the Technology sector demonstrated a remarkable 95% reduction, achieving a final PPP of just 4.25%
Key Takeaways
- Sustained cybersecurity training significantly reduces phishing vulnerability across all industries and company sizes, with large companies showing the most dramatic improvements over time
- Critical infrastructure sectors face increasing sophisticated cyberattacks, prompting legislative action and increased government support for cybersecurity awareness and defense mechanisms
- International collaboration, particularly through the Five Eyes alliance, and investments in building a skilled cybersecurity workforce are crucial strategies adopted by both countries to address evolving cyber threats and build long-term resilience