CTB-Locker (Curve-Tor-Bitcoin Locker) is also known as Critoni.A. This particular ransomware was discovered midsummer 2014 by Fedor Sinitisyn, a security researcher for Kaspersky.
From spam emails with an infected .zip file attached, CTB-Locker installs itself to its victims’ computers and immediately begins encrypting their files by using elliptic curve cryptography. Once the ransomware has infected a computer and locked a victim’s files, the victim will see a screen displayed on the monitor—and this screen explains that the computer’s files have been encrypted with “strongest encryption” and a decryption key that has been uniquely generated for the victim’s computer. The key, reads the notice, is stored somewhere on the internet, and the computer’s files cannot by decrypted until the victim purchases the key. The notice also claims that any attempts by the victim to rid the infected computer of the ransomware will result in the destruction of the decryption key and the victim permanently losing his or her computer’s files. Interestingly, this notice grants victims of CTB-Locker the option to read it in a different language, including English and Russian.
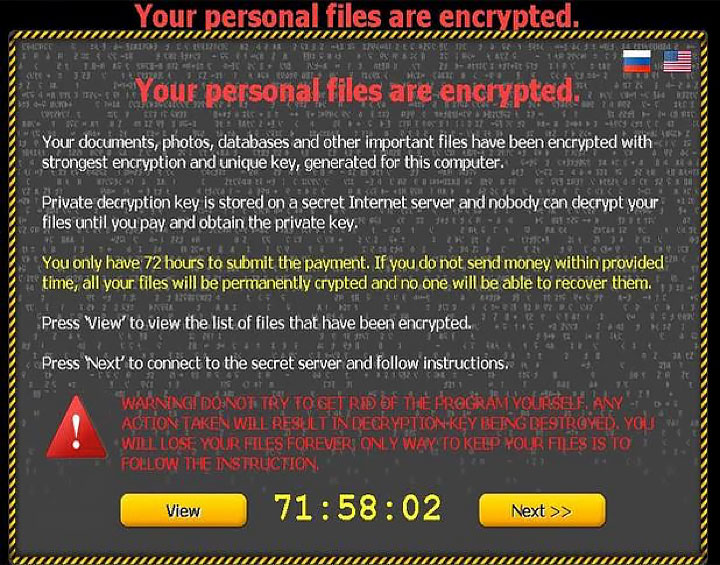
The cyber criminal behind the scheme demands a payment of anywhere between two to three bitcoin, which is roughly $489-$734. More recent CTB-Locker infections require the victim to pay a higher ransom, closer to 3 bitcoin, as opposed to lower ransoms of around 0.2 bitcoin when the ransomware first started infecting computers. In addition, those whose devices are infected with CTB-Locker only have a couple of days to pay the ransom. Otherwise, threaten the cyber criminals, victims will never be able to access their files again. There’s also another catch—the decryption key that is supposed to be purchased by the victim will only last for about 96 hours. After that, it expires and is deleted from the server hosting it. If victims do not act immediately once they have purchased the decryption key, then their files will remain encrypted.
As of right now, nobody really knows where this ransomware came from. Earlier versions of it only had an English language GUI; but later, Russian was added. As of March 3, 2015, CTB-Locker has been infecting computers located in France and Spain as well. As of April 2016, an update to CTB-Locker uses blockchain to deliver decryption keys for their victims
The worst CTB-Locker infections were mainly in Russia, so it’s most likely that the developers were from an eastern European country. On another note, CTB-Locker’s country of origin is probably not Russia, due to the fact that the Russian security services immediately arrest and shut down any Russians hacking others in their own country.
Update: free CTB-Locker decryption instructions are available!
